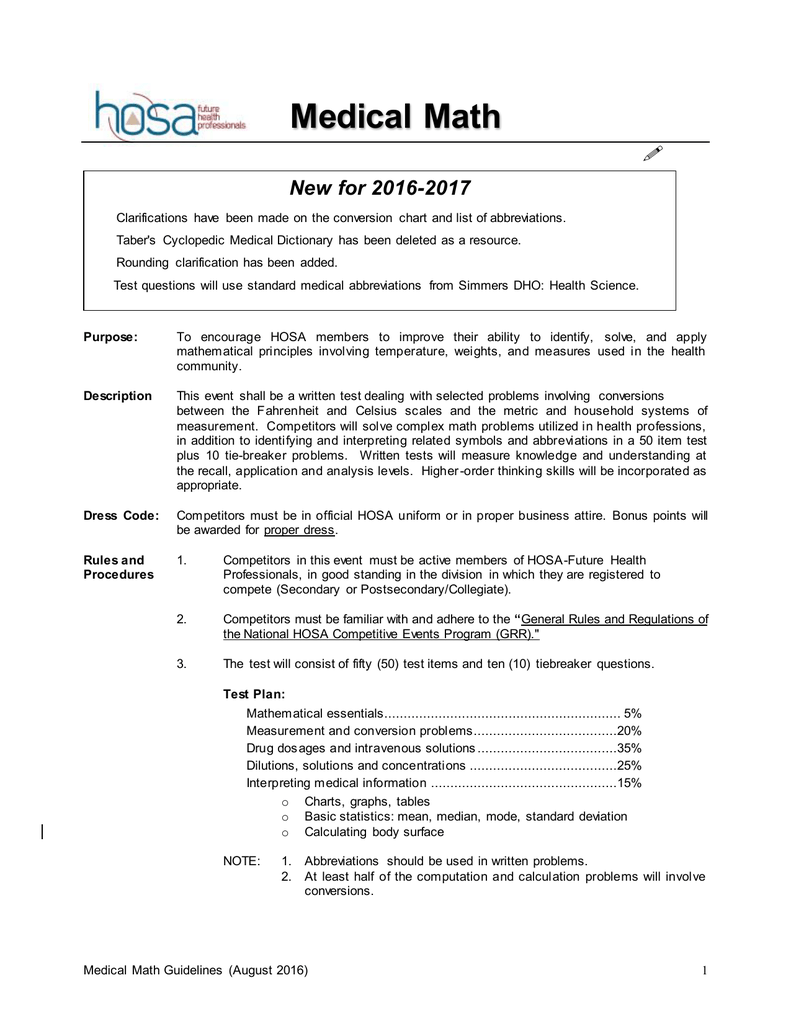
Medical math is an essential component of healthcare education, particularly in Chapter 13, where healthcare professionals delve into the intricacies of calculations for medication dosages, fluid management, and other critical aspects of patient care. Whether you're a nursing student, pharmacist, or physician, understanding this chapter thoroughly can significantly improve patient safety and clinical outcomes. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of Chapter 13 medical math, ensuring you grasp its concepts with ease.
For healthcare providers, mastering medical math isn't just about passing exams; it's about ensuring the well-being of patients. Errors in calculations can lead to severe consequences, making proficiency in this area crucial. Chapter 13 of medical math focuses on practical applications, equipping learners with the tools they need to make accurate calculations in real-world scenarios.
This guide will take you through the fundamental principles of Chapter 13 medical math, breaking down complex topics into digestible sections. By the end of this article, you'll have a solid understanding of how to apply these concepts effectively, enhancing your confidence and competence in clinical practice.
Read also:White Arches Caravans Northampton
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Chapter 13 Medical Math
- Key Concepts in Chapter 13 Medical Math
- Dosage Calculations and Conversions
- Intravenous Fluids and Rate Calculations
- Pediatric Dosage Calculations
- Common Errors in Medical Math
- Tools and Resources for Learning
- Real-World Applications of Chapter 13 Medical Math
- Effective Study Tips for Chapter 13
- Conclusion
Introduction to Chapter 13 Medical Math
Chapter 13 medical math serves as a cornerstone for healthcare professionals, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. This section introduces the primary objectives of this chapter, emphasizing its importance in clinical practice. Understanding the basics of medical math ensures that healthcare providers can make accurate calculations, minimizing the risk of errors.
Key areas covered in this chapter include dosage calculations, unit conversions, and intravenous therapy management. Each of these topics plays a vital role in patient care, requiring meticulous attention to detail. As you progress through this article, you'll discover how each concept builds upon the other, creating a comprehensive framework for mastering medical math.
Key Concepts in Chapter 13 Medical Math
Understanding Basic Mathematical Principles
Before diving into the specifics of Chapter 13, it's essential to review basic mathematical principles that form the foundation of medical math. These principles include fractions, decimals, ratios, and proportions. Familiarity with these concepts is crucial for tackling more complex calculations.
- Fractions: Used in dosage calculations, fractions help determine precise amounts of medication.
- Decimals: Often used in representing medication dosages, understanding decimal points is critical for accuracy.
- Ratios and Proportions: These are essential for converting units of measurement and calculating medication dosages.
Unit Conversions in Medical Math
Unit conversions are a fundamental aspect of Chapter 13 medical math. Healthcare professionals frequently encounter situations where they need to convert between different units of measurement, such as milligrams to grams or milliliters to liters. Mastery of these conversions ensures that medication dosages are administered safely and effectively.
Some common conversions include:
- 1 gram (g) = 1000 milligrams (mg)
- 1 liter (L) = 1000 milliliters (mL)
- 1 kilogram (kg) = 1000 grams (g)
Dosage Calculations and Conversions
One of the most critical aspects of Chapter 13 medical math is dosage calculations. This section explores the methods used to calculate medication dosages accurately, ensuring patient safety. Dosage calculations involve determining the correct amount of medication to administer based on the patient's weight, age, and other factors.
Read also:Dylan Jones Simi Valley
Key formulas for dosage calculations include:
- Desired dose = (Prescribed dose / Available dose) × Quantity
- Weight-based dosing: (Patient weight × Dosage per kilogram) = Total dose
Intravenous Fluids and Rate Calculations
Understanding Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous (IV) therapy is a common practice in healthcare, requiring precise calculations to ensure the correct flow rate and volume of fluids administered. This section delves into the intricacies of IV therapy, covering topics such as drip rates, infusion times, and fluid volume calculations.
Calculating IV Drip Rates
Calculating IV drip rates involves determining the number of drops per minute required to deliver the prescribed volume of fluid over a specified time. The formula for calculating drip rates is:
Drip rate = (Volume to be infused × Drop factor) / Time in minutes
This calculation ensures that the IV infusion is administered at the correct rate, preventing complications such as fluid overload or dehydration.
Pediatric Dosage Calculations
Pediatric patients require special consideration when it comes to medication dosages. Due to their smaller size and developing physiology, precise calculations are essential to avoid adverse effects. Chapter 13 medical math addresses pediatric dosage calculations, providing guidelines for safe and effective medication administration in children.
Key considerations in pediatric dosage calculations include:
- Weight-based dosing: Calculating medication dosages based on the child's weight.
- Body surface area (BSA): Using BSA to determine appropriate dosages for certain medications.
- Age-appropriate dosing: Adjusting dosages based on the child's age and developmental stage.
Common Errors in Medical Math
Errors in medical math can have serious consequences, emphasizing the need for vigilance and accuracy. This section highlights common mistakes made in calculations and provides strategies for avoiding them. By understanding these pitfalls, healthcare professionals can enhance their proficiency in medical math and reduce the risk of errors.
Some common errors include:
- Incorrect unit conversions
- Miscalculations in dosage amounts
- Failure to double-check calculations
Tools and Resources for Learning
Utilizing Technology for Medical Math
Modern technology offers numerous tools and resources to aid in learning medical math. From mobile apps to online calculators, these resources can help healthcare professionals practice and refine their calculation skills. Incorporating technology into your study routine can enhance your understanding of Chapter 13 medical math and improve your confidence in clinical settings.
Recommended Resources
Some recommended resources for learning medical math include:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI): A trusted source for medical research and educational materials.
- Mayo Clinic: Offers valuable insights into medical math and its applications in healthcare.
- Khan Academy: Provides free educational content, including tutorials on mathematical concepts relevant to medical math.
Real-World Applications of Chapter 13 Medical Math
Understanding the real-world applications of Chapter 13 medical math is crucial for healthcare professionals. This section explores how the concepts learned in this chapter are applied in clinical practice, highlighting their importance in ensuring patient safety and improving outcomes.
Examples of real-world applications include:
- Administering medications in hospital settings
- Calculating fluid requirements for critically ill patients
- Adjusting dosages for patients with renal or hepatic impairments
Effective Study Tips for Chapter 13
Mastering Chapter 13 medical math requires dedication and effective study strategies. This section provides tips and techniques for learning and retaining the material, ensuring success in both academic and clinical settings.
Some effective study tips include:
- Practice regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering medical math.
- Seek help when needed: Don't hesitate to ask for assistance from instructors or peers.
- Use visual aids: Diagrams and charts can help clarify complex concepts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Chapter 13 medical math is a critical component of healthcare education, providing the foundation for accurate and safe medication administration. By understanding the key concepts, practicing regularly, and utilizing available resources, healthcare professionals can enhance their proficiency in medical math and improve patient outcomes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into healthcare education and practice. Together, we can elevate the standards of medical care and ensure the well-being of patients worldwide.